Syria stands formally accused of violating the Chemical Weapons Convention
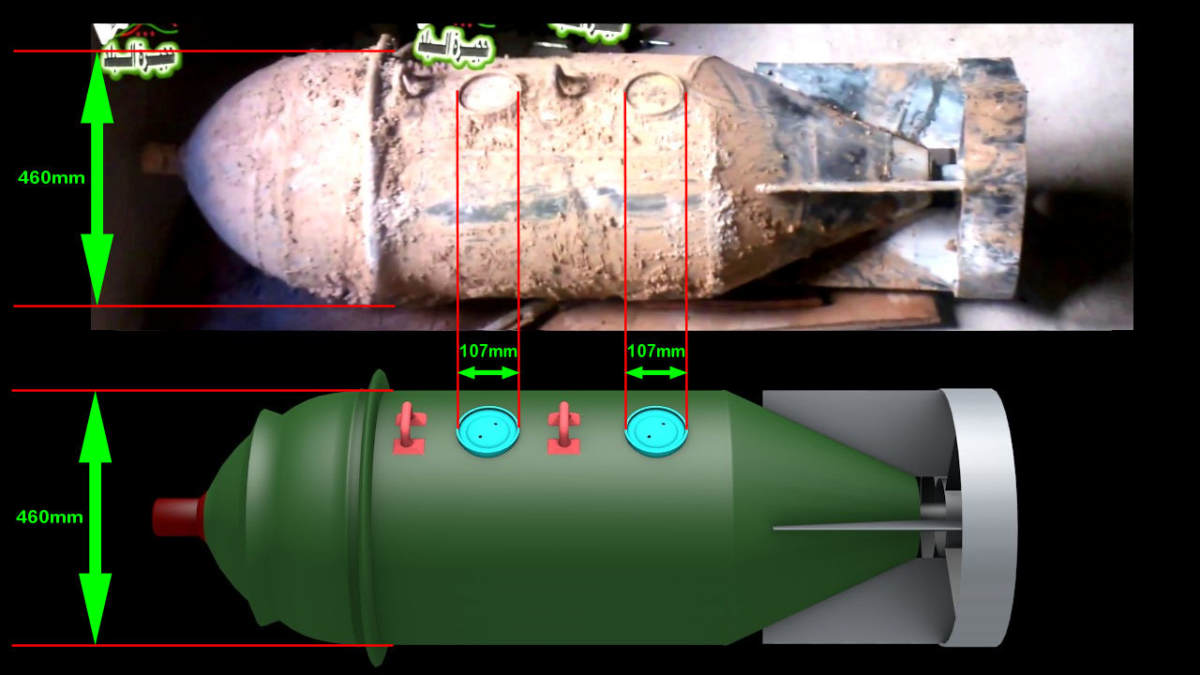
The Executive Council of the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) held its 94th session from 7–10 July. Prominent on the agenda was the determination by the Investigation and Identification Team (IIT) that ‘there are reasonable grounds to believe’ that Syrian government forces bear responsibility for several chemical weapon (CW) attacks at the end of March 2017. The finding is the first time that the Technical Secretariat of the OPCW has formally charged a state party to the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC) with violating Article I, para. 1(b) to never under any circumstances use CW. The accusation is …
From irritant to tear-gas: the early story of why a toxic agent became non-lethal
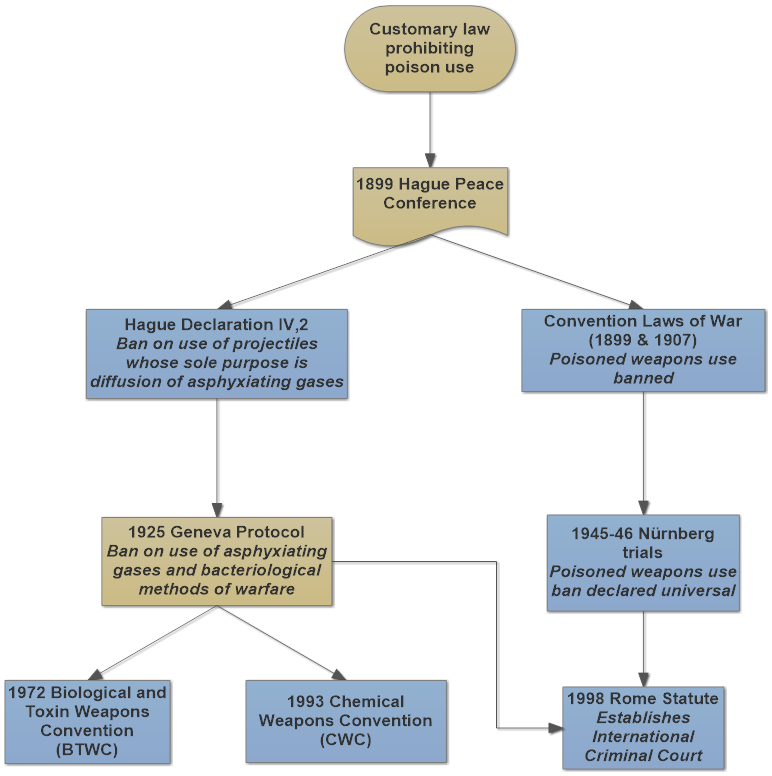
With the recent international attention to riot control agents (RCA) people have raised the question how their use against protesting civilians can be legal when the toxic agents are internationally banned from battlefields. Framed as such, the question is not entirely correct. In my previous blog posting I argued that outlawing RCAs for law enforcement and riot control based on the above reasoning may run into complications in the United States because the country still identifies operational military roles for irritants on the battlefield in contravention of the Chemical Weapons Convention. This article sketches the convoluted history of harassing agents …
‘Tear-gas’: authorised at home, banned in war? Not so for the USA
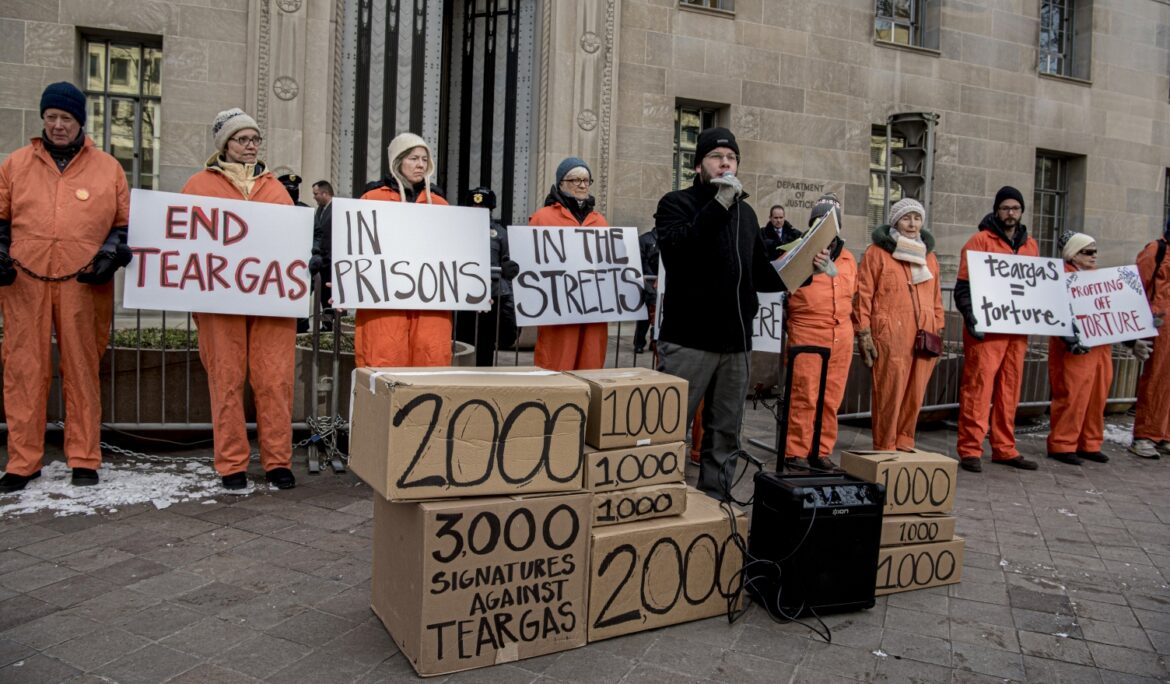
‘Tear-gas’ may come to symbolise the Trump Administration’s heavy-handed response to the popular reaction against the killing of George Floyd, a middle-aged black man, by a white police officer. The President’s rolling thunder of insensitive, divisive tweets extolling law and order and deriding the legitimate demands by the Black Lives Matter movement has contributed to irresponsible use of force against essentially peaceful protesters, onlookers, and members of the press. Police brutality combined with widespread lack of accountability – unless a person gets killed or an incident is captured on media – has led to multiple types of excesses. When President …
JPPR – The 4 letters that shaped my career
Dazed. Shocked. Stunned. Does any one of these words even begin to convey my reaction when around noon on 23 April I received the phone call informing me of Julian’s passing, having lost the battle against COVID-19 the night before? When I entered the field of chemical and biological warfare in 1986, his name immediately stood out. Julian Perry Robinson, a name immediately associated with the Stockholm International Peace research Institute (SIPRI) and the University of Sussex, near Brighton in the south of England. Our first encounter was in 1989. In hindsight, it was unsurprisingly at a workshop bringing together …
A Middle East Zone Free from Non-conventional Weapons (4)
Part 4: Clear legal definitions at the core of the future treaty This article is the fourth in a series of blog postings exploring the opportunities and challenges facing a new series of conferences at the United Nations in New York to eliminate non-conventional arms – essentially nuclear weapons, and to a lesser extent chemical and biological weapons (CBW) – from the military arsenals in the Middle East. Why legal definitions matter By adopting Decision 73/546 on 22 December 2018, the UN General Assembly tasked the newly established conference with ‘elaborating a legally binding treaty establishing a Middle East …
A Middle East Zone Free from Non-conventional Weapons (3)
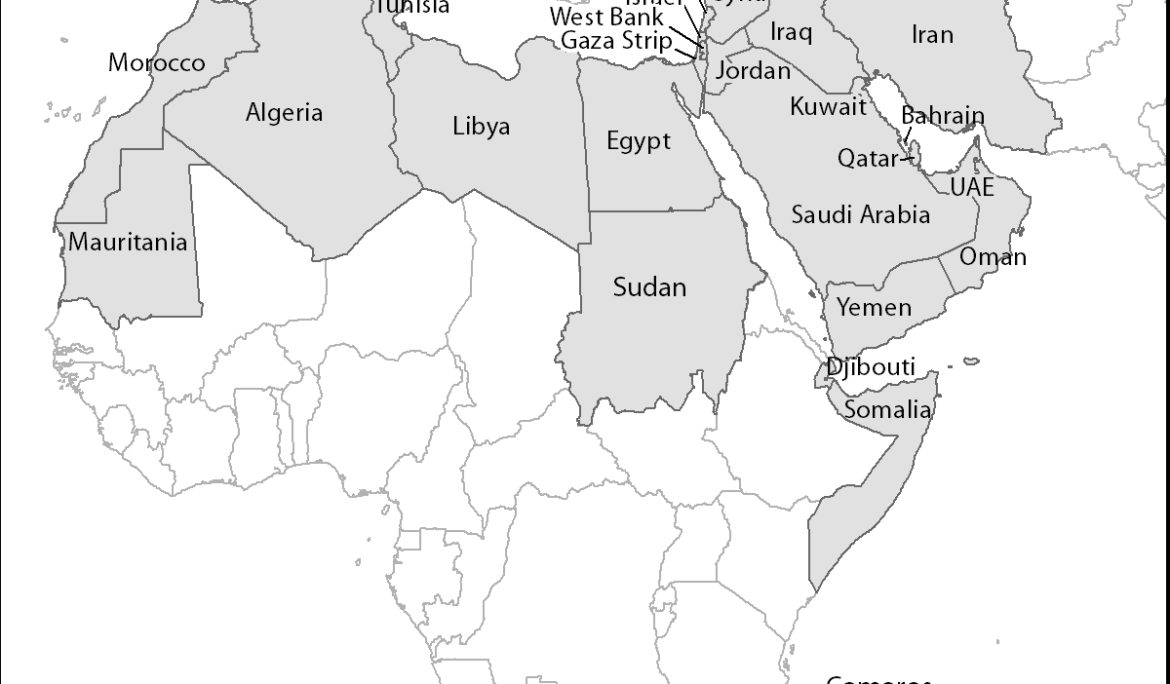
Part 3: Defining the Middle East, a loaded question In November 2019 a conference at the United Nations in New York (report here) marked a fresh round of diplomatic efforts to eliminate non-conventional arms – essentially nuclear weapons, and to a lesser extent chemical and biological weapons (CBW) – from the military arsenals in the Middle East. As indicated in the second part of this series, participants in the new conference series depart from the definition of the Middle East used by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). At the UN Institute for Disarmament Research (UNIDIR) seminar ‘The Middle …
A Middle East Zone Free from Non-conventional Weapons (2)
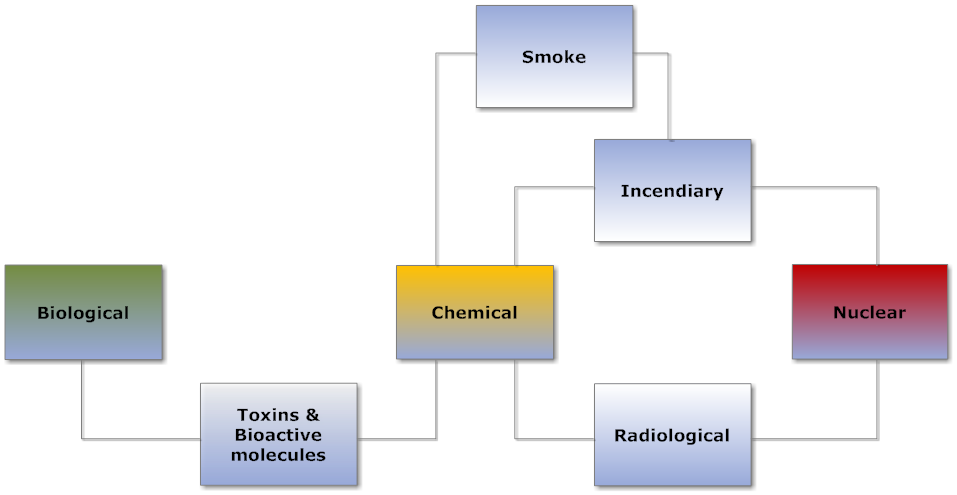
Part 2: Treaties governing chemical and biological weapons In November 2019 a conference at the United Nations in New York marked a fresh round of diplomatic efforts to eliminate non-conventional arms – essentially nuclear weapons, and to a lesser extent chemical and biological weapons (CBW) – from the military arsenals in the Middle East. This article is the second in a series of blog postings exploring the opportunities and challenges to ensure that the regional risks of CBW threats and use – chemical weapons (CW) were and, as I am writing, are part of conflicts in the Middle East …
A Middle East Zone Free from Non-conventional Weapons (1)
Part 1: A new process to disarm the Middle East In November 2019 a conference at the United Nations in New York marked a fresh round of diplomatic efforts to eliminate non-conventional arms – essentially nuclear weapons, and to a lesser extent chemical and biological weapons (CBW) – from the military arsenals in the Middle East. The previous initiative died in 2015 as the review conference (RevCon) of the 1968 Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) failed to agree on a consensus document. The new series of annual meetings takes place outside the NPT RevCon cycle, which consists of a quinquennial …